The following page provides code snippets describing how to run batches of indicators directly from MobyDQ GraphQL API.
If you run MobyDQ on your local machine, the API can be accessed at the following URLs.
| Component | Docker on Linux / Windows Pro | Docker on Windows Home |
|---|---|---|
| GraphQL API Documentation | https://localhost/graphiql | https://your_docker_machine_ip/graphiql |
| GraphQL API | https://localhost/graphql | https://your_docker_machine_ip/graphql |
Manual Example
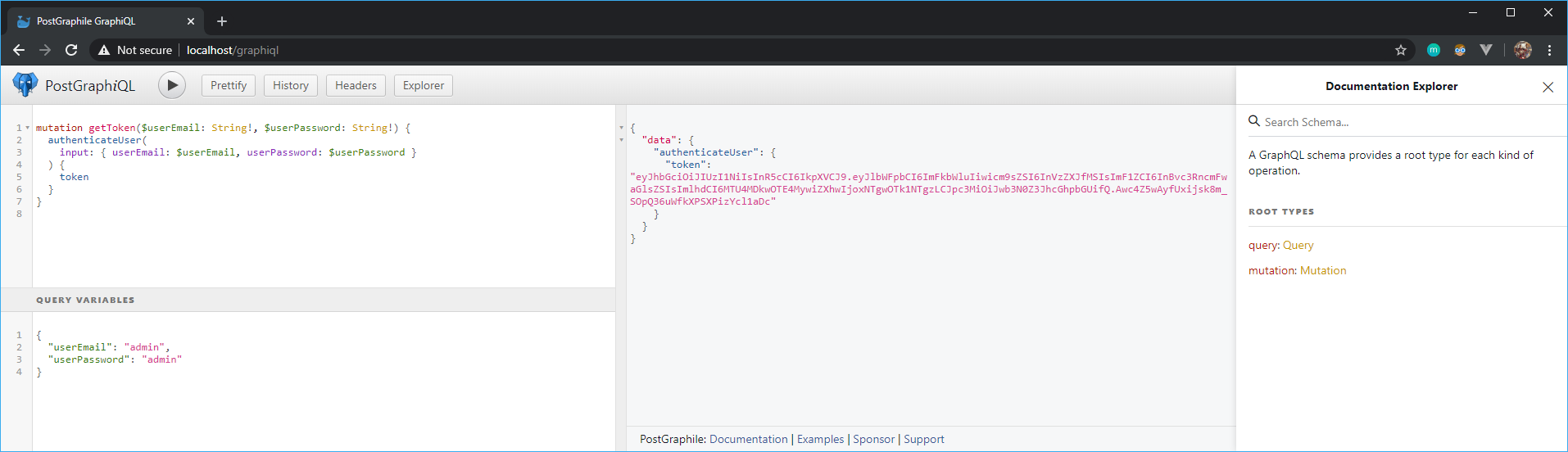
Navigate to GraphiQL from which you can manually execute http requests (cf. links above). The first step is to call the mutation authenticateUser to retrieve a valid token.
mutation getToken {
authenticateUser(input: { userEmail: "admin", userPassword: "admin" }) {
token
}
}
In the screenshot below, the userEmail and userPassword arguments are provided dynamically through variables.
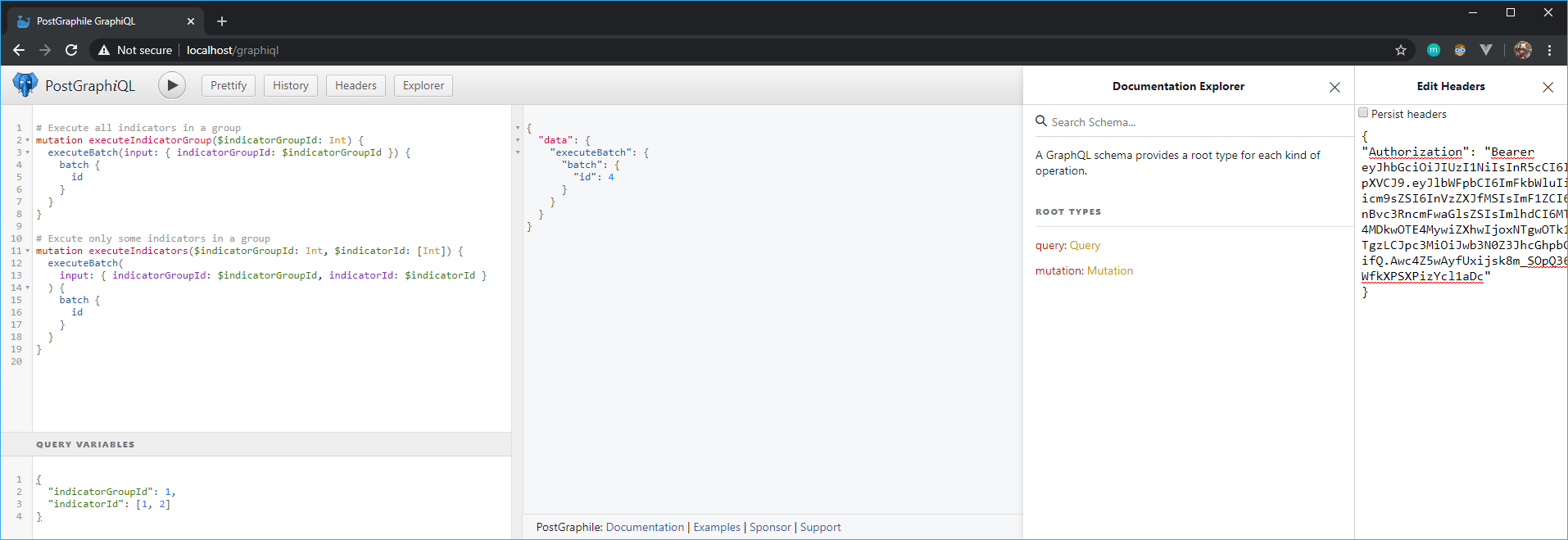
In the horizontal menu at the top of the page, click on “Headers” to display the http headers parameters. Update the Authorization parameter so that it includes the token generated in the previous step {"Authorization": "Bearer <token>"}.
Finally call the mutation executeBatch with an indicator group Id provided in the input parameters. You can get the indicator group Id from the indicator group page in the web application. The input parameters can also include a list of indicator Ids to run only specific indicators from the indicator group.
Note: the http request must return the batch Id as in the example below to ensure the batch is properly executed.
# Execute all indicators in a group
mutation executeIndicatorGroup {
executeBatch(input: { indicatorGroupId: 1 }) {
batch {
id
}
}
}
# Excute only some indicators in a group
mutation executeIndicators {
executeBatch(input: { indicatorGroupId: 1, indicatorId: [1, 2] }) {
batch {
id
}
}
}
In the screenshot below, the indicatorGroupId and indicatorId arguments are provided dynamically through variables.
Python Example
The python code snippet below follows the same logic as described in the manual example.
import requests
url = 'https://localhost/graphql'
headers = { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }
# Inputs for authentication
user_email = 'admin'
user_password = 'admin' # Do not do this in production!
# Payload for authentication
payload = {}
payload['query'] = '''mutation getToken($userEmail: String!, $userPassword: String!){authenticateUser(input:{userEmail: $userEmail, userPassword: $userPassword}){token}}'''
payload['variables'] = {}
payload['variables']['userEmail'] = user_email
payload['variables']['userPassword'] = user_password
# Execute http request and get token
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload)
data = response.json()
token = 'Bearer ' + data['data']['authenticateUser']['token']
# Inputs for batch execution
indicator_group_id = 1
indicators = [1, 2]
# Payload for batch execution
payload = {}
payload['query'] = '''mutation executeIndicators($indicatorGroupId: Int, $indicatorId: [Int]){executeBatch(input:{indicatorGroupId: $indicatorGroupId, indicatorId: $indicatorId}){batch{id}}}'''
payload['variables'] = {}
payload['variables']['indicatorGroupId'] = indicator_group_id
payload['variables']['indicatorId'] = indicators
# Set authorization header and execute http request
headers['Authorization'] = token
response = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=payload)
data = response.json()
print(data)
JavaScript Example
To be documented.